No products in the cart.
Need help? Call us:
+1 (833) 763-7837
Menu
Categories
- Accessories
- Air Purification Accessories
- Antennas
- Attenuators
- Barcode Scanners
- Batteries and Chargers
- Bottles and Dispensers
- Cables - Misc
- Carrying Straps, Lanyards and Harnesses
- Carts
- Case and Cart Accessories
- Cases
- Cathodic Protection Accessories
- Coaxial
- Crimper Accessories
- Datacom Accessories
- Dry Block Bath Inserts
- EMI Accessories
- Enclosure Accessories
- FIber Optic Accessories
- Fiber Optic Cables
- Gas Detection Accessories
- General Accessories
- GPIB Adapters
- Heating Elements
- Hipot Accessories
- Hoses - Miscellaneous
- HVAC Accessories
- Induction Heater Accessories
- Input Cards
- Jacks /Adapters /Plugs /Clips /Terminators/Coaxial
- Jobsite Storage and Cabinets
- Knockout Accessories
- Lab Accessories
- LCR Test Fixtures
- LED and LCD Displays
- Manuals
- Material Handling Accessories
- Microphones
- Microscope Accessories
- Motors
- Options
- Pinhole/Holiday Detector Accessories
- Plumbing Accessories
- Precision Measuring Instrument Accessories
- Pressure Calibrator Modules
- Printers and Printing Supplies
- Probes
- Rack Mounts and Stands
- Repair Parts and Fuses
- Scale Accessories
- Shunts
- Software
- Soldering Accessories
- Spectrum Analyzer Accessories
- Static Control Accessories
- Switch and Semiconductor Modules/Access
- Test Fixtures
- Test Leads and Instrument Accessory Kits
- Thermal Imager Accessories
- Training and Education
- Underground Utility Location Accessories
- Vibration Accessories
- Video Accessories
- Voltage Transformer
- Warranty and Calibration
- Amplifiers / Preamps / Preamplifiers
- Audio Equipment
- Automotive Test Tools
- Battery Testing
- Blower Door and Duct Testing
- Borescopes / Boroscopes
- Clamp Meters
- Cleanroom
- Color and Appearance
- Conduit Benders
- Current Sensors
- Datacom and Networking Products
- Dataloggers Data Acquisition
- Decade Boxes
- Distance Meter
- Electrical Parts and Products
- Cable and Wire
- Cable Reels
- Electrical Cord
- Electrical Jumpers and Pigtails
- Electrical Parts
- Electrical Plugs and Connectors
- Line Splitters
- Lockout / Tagout
- Outlet Boxes
- Pulling Products
- Pushbutton Pendant Stations
- Receptacle Testers
- Temporary Power Distribution
- Terminal Blocks and Strips
- Terminals and Crimps
- Wall Plates
- Wire Management
- Wire Ties
- Work Lighting and String Lighting
- Enclosures and Boxes
- Environmental Testers / Physical Property
- Anemometer / Air Flow
- Barometers and Altimeters
- Chlorine Tester
- Dissolved Oxygen Meter / Fluoride
- EMF / ELF Meter
- Heat Index Monitors
- Humidity Meters
- Hygrometers
- Moisture Meters
- Nuclear Radiation Monitors
- PH / ORP Meters
- Psychrometer
- Refractometers / BRIX
- Scales / Weight
- Sound Level Meters
- Stopwatches / Timers / Clocks
- Water Quality Accessories
- Water Quality Meters
- Weather Measurement
- Wind Tunnels
- Flow Measurement
- Force / Torque / Hardness Meters
- Gas Detection
- Ground Testers
- Health and Safety
- HVAC Equipment and Instruments
- Automotive RRR Machines
- Brazing
- Combustion Analyzers
- Hose Adapters, Valves and Parts
- HVAC - Testing - Adjusting - Balancing
- HVAC Equipment - Misc
- HVAC Manifolds and Gauges
- HVAC Vacuum Pumps
- Refrigerant Leak Detectors
- Refrigerant Recovery Machines
- Refrigerant Recovery Tanks
- Smoke Pump Test Kits
- Tubing Tools
- Vacuum Gauges
- Hydraulic Cylinders
- Indoor Air Quality
- LCR Meters / Impedance Measurement Products
- Leakage Detectors
- Life Sciences Equipment
- Autoclaves and Sterilization
- Bunsen Burners
- Centrifuges
- Cold Storage
- Colony Counters
- Dry Block Heaters and Cooling Blocks
- Environmental Test Chambers
- Flame Photometers
- Flocculators
- Fluidized Bed Baths
- Gel Imaging Electrophoresis
- Glassware Washers-Dryers
- Heating Mantles / Electromantles
- Homogenizers
- Incubators
- Kjeldahl Apparatus
- Lab Apparatus - Misc
- Laboratory Ovens
- Laboratory Pumps
- Laboratory Water Purification Systems
- Magnetic Bead Based Purification
- Melting Point Apparatus
- Mixers Rotators and Stirrers
- Pipettes
- Reaction Station
- Recirculating Chillers / Coolers
- Refrigerated Heating Circulators
- Rotary Evaporators
- Shakers and Rockers
- Slide Warmers
- Spectrophotometer
- Thermal Cycler / PCR
- Titrators
- Water Baths and Liquid Baths
- Logic Analyzers
- Materials Testing
- Megohmmeter / Insulation Resistance Testers
- Micro-Ohmmeter / Milliohmmeter
- Microscopes
- Multimeters
- Network Analyzer
- Oscilloscopes
- Panel Meters
- Personal Protective Equipment
- Phase / Motor / Transformer Testing
- Power Measurement
- Power Supplies
- Process / Calibration
- Programmers / IC and RAM Testers
- Protocol Analyzers
- Prototyping
- Radiometric
- Reliability / Preventative Maint / Rotational
- RF, Microwave, EMI
- Safety Testing / Surge Testing
- Signal Generators / Counters
- Signal Level Meters - CATV / CCTV / Satellite
- Solar Analyzers
- Soldering Equipment
- BGA Rework Station
- Chemicals
- Cleaning Pins and Drills
- Depaneling Systems
- Desoldering Equipment/Rework Stations
- Desoldering Irons
- Dispensing Equipment
- Flux
- Flux Remover
- Fume Extraction
- Hot Air Guns
- Hot Air Pencils
- Lead Forming Equipment
- Nitrogen Generation
- Nozzles
- PCB Supports and Holders
- Pre-Heater
- Solder
- Solder Wick
- Soldering Equipment
- Soldering Irons
- Soldering Pots
- Soldering Robots
- Soldering Stands
- Soldering Stations
- Soldering Tip Cleaners
- Soldering Tip Thermometers
- Soldering Tweezers
- Sponges and Brass Wool
- Thermal Wire Strippers
- Tips
- Vacuum Pick-Up Tools
- Sporting / Hunting / Law Enforcement Optics
- Static Control
- Surveying / Construction Measurement
- Thermal Imagers
- Thermometers
- Thickness Gauges
- Tools
- Blackeners
- Cable Cutters
- Cable Strippers
- Cable Tie Guns
- Combination Squares
- Conduit Tools
- Crimpers
- Cutters
- Cutting Tools
- Datacom / Fiber Optic Tools
- Drill Bits and Sets
- Drill Rod
- Dry Lubricants
- Electric Screwdrivers
- Feeler Gage
- Fiber Optic Cable Tools and Fiber Scopes
- Flashlights and Headlights
- Ground Flat Stock
- Hex Drivers, Torx Drivers
- Hose Benders
- Hose Clamps
- Hot Melt
- HVAC Service Tools
- Insulated Tools
- Keystock
- Knockout Tools
- Layout Fluid
- Level Measurement
- Maintenance Kits
- Multi-Tools
- Other Hand Tools
- Pliers
- Pneumatic Hand Tool Operators
- Power Tools
- Probes & Scribes
- Punch & Die Sets
- Punchdown Tools
- Remote Hydraulic Pumps
- Screwdrivers
- Shims & Shim Stock
- Sockets & Ratchets
- Spatulas
- Telecom Service Tools
- Telescopic Tools
- Threaded Rod
- Tool Kits
- Tool Wrap
- Tweezers
- Vises
- Wire
- Wire Strippers
- Wrenches & Wrench Sets
- Toys / Cool Stuff
- Transmission Line/Station Testing
- Cable Testing
- Circuit Breaker Testers
- Corona Detection
- Dielectric Oil Testing
- High Current Detectors / Indicators
- High Voltage Detectors / Indicators
- Hot Sticks
- Phasing Sticks
- Primary Injection Test Equipment
- Safety Equipment
- Secondary Injection Test Equipment
- SF6 Gas Leak Detectors
- Transformer Testing/TTR
- Transmission Cable Height Meters
- Video Distribution Equipment
- Video Test Equipment
- Voltage / Continuity and Non-Contact Testers
- Wire Tracers / Circuit Breaker Tracers
- Workbenches
Digilent MCC 172 w/ cables – 24-Bit IEPE Measurement DAQ HAT w/ 2 Coaxial Cables for Raspberry Pi
Brand:
35 people are viewing this product right now
$492.80
Shipping calculated at checkout.
Estimated delivery:5 days
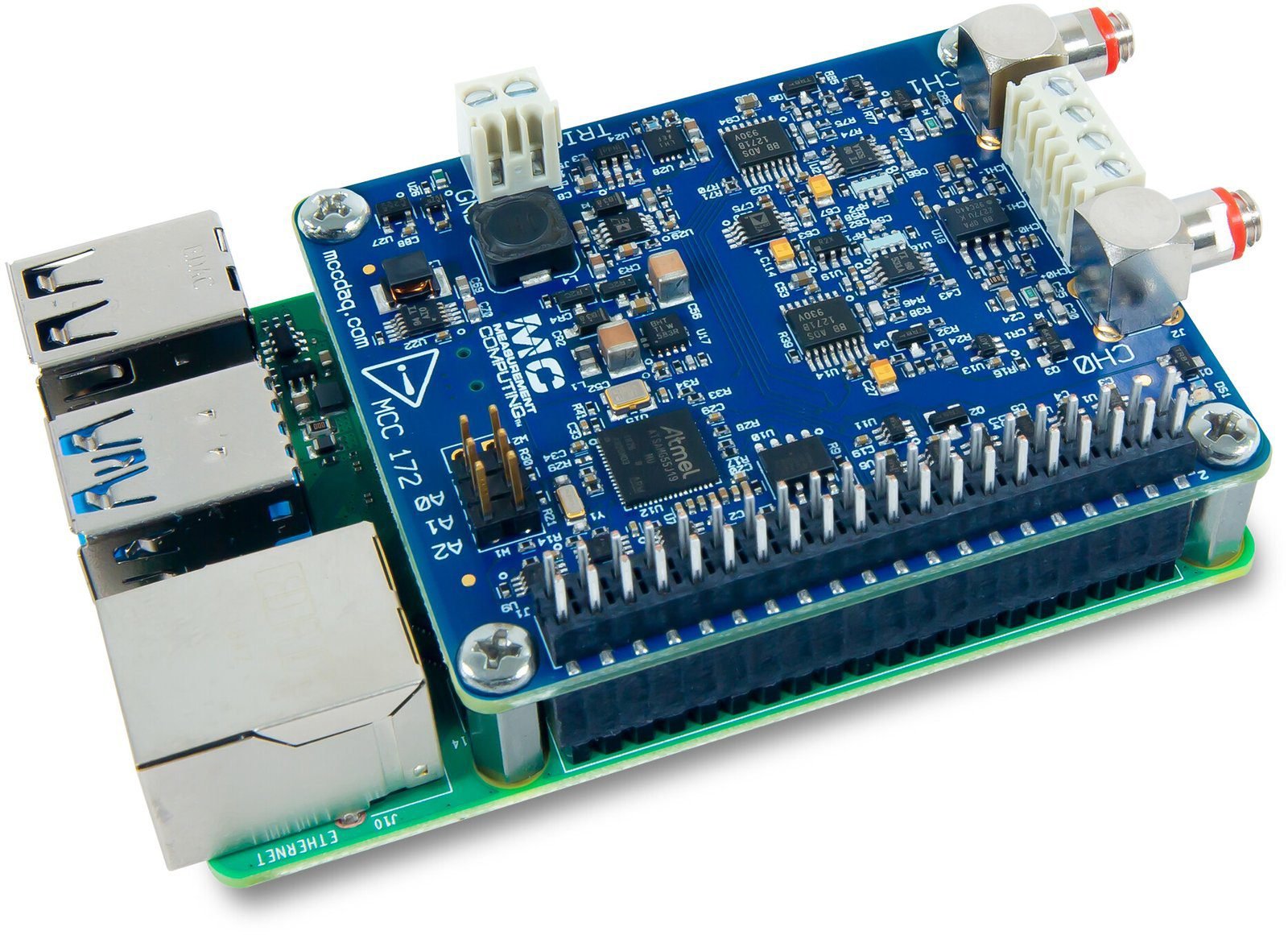
MCC 172: IEPE Measurement DAQ HAT for Raspberry Pi with two coaxial cables
- Comes with two coaxial cables
- Two IEPE inputs
- Two 24-bit, 51.2 kS/s A/D converters (one per channel)
- AC coupled at ±5 V
- 10-32 and screw terminal connections for OEM support
- Synchronous ADC conversions between multiple boards
- Onboard sample buffers allow high-speed acquisition
- External digital trigger input
SKU:
Digilent MCC 172 w/ cables
Tags: Dataloggers Data Acquisition, Voltage Datalogger
Categories: Voltage Datalogger
Have any Questions?
Feel free to Get in touch
Guarantee Safe and Secure Payment Checkout
Description

Digilent MCC 172 w/ cables
- Comes with two coaxial cables
- Two IEPE inputs
- Two 24-bit, 51.2 kS/s A/D converters (one per channel)
- AC coupled at ±5 V
- 10-32 and screw terminal connections for OEM support
24-Bit IEPE Measurement DAQ HAT w/ 2 Coaxial Cables for Raspberry Pi
The Measurement Computing MCC 172 is a voltage HAT (Hardware Attached on Top) designed for use with Raspberry Pi®. The MCC 172 features two channels for making sound and vibration measurements from IEPE sensors like accelerometers and microphones. The two 24-bit differential analog input channels simultaneously acquire data at rates up to 51.2 kS/s. Users can turn the IEPE excitation current on or off. Each channel has a dedicated A/D converter. Both ADCs share the same clock and are synchronized to start conversions at the same time for synchronous data. Multiple MCC 172 HATs can be synchronized to a single sampling clock. The clock is programmable for sampling rates between 51.2 kS/s to 200 S/s. The trigger input (terminal TRIG) is used to delay an input scan until a specified condition is met at the trigger input.
HAT configuration parameters are stored in an onboard EEPROM that allows the Raspberry Pi to automatically set up the GPIO pins when the HAT is connected. The open-source MCC DAQ HAT Library of commands in C/C++ and Python allows users to develop applications on the Raspberry Pi using Linux. The MCC DAQ HAT Library supports operation with multiple MCC DAQ HATs running concurrently. Console-based and user interface (UI) example programs are available for each API.
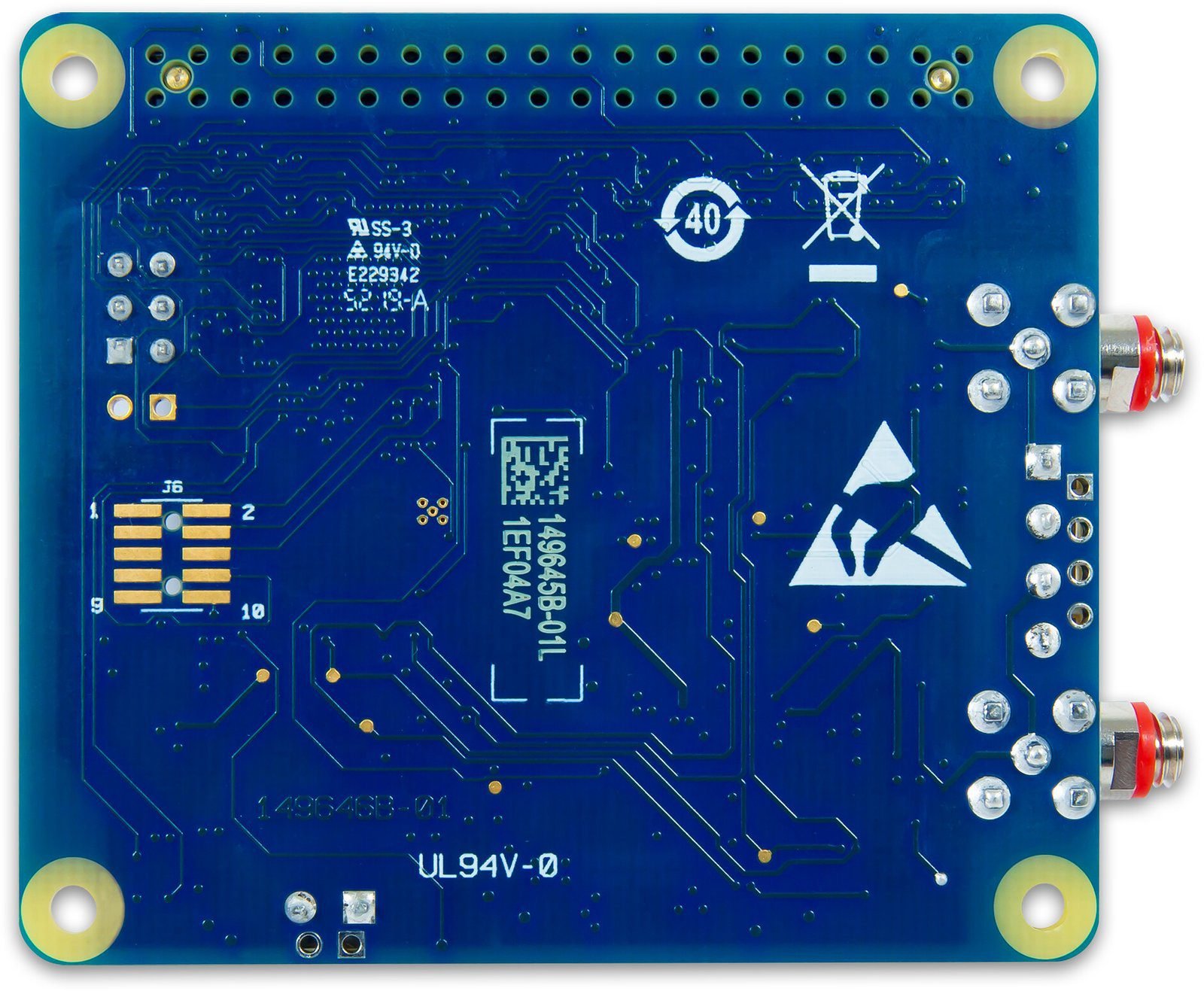
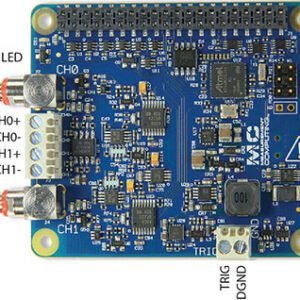
Board components
10-32 Coaxial Connectors
- CH0 and CH1 (CHx): Analog input connectors (do not connect an input source to the 10-32 connectors and screw terminals at the same time).

Screw Terminals
- CH0+/CH0- and CH1+/CH1- (CHx+/CHx-): Analog input terminals (do not connect an input source to the 10-32 connectors and screw terminals at the same time).
- Trigger (TRIG): External digital trigger input terminal. The trigger mode is software configurable for edge or level sensitive, rising or falling edge, high or low level.
- DGND (GND): Digital ground for the trigger terminal.
Address Jumpers
- A0 to A2: Used to identify each HAT when multiple boards are connected. The first HAT connected to the Raspberry Pi must be at address 0 (no jumper). Install jumpers on each additional connected board to set the desired address.
Status LED
The LED turns on when the board is connected to a Raspberry Pi with external power applied and flashes when communicating with the board. The LED may be blinked by the user.
Header Connector
The board header is used to connect with the Raspberry Pi.

Functional Details
ADC Clock
The ADCs on a board share the same clock and are synchronized to start conversions at the same time for synchronous data. The clock and synchronized signals may also be shared across the Raspberry Pi GPIO header to synchronize multiple MCC 172s. The clock is programmable for various sampling rates between 51.2 kS/s and 200 S/s.
Trigger
The trigger input (terminal TRIG) is used to hold off the beginning of an analog input scan until the desired condition is met at the trigger input. The trigger input signal may be a 3.3V or 5V TTL or CMOS logic signal. The input condition may be a rising edge, falling edge, high level, or low level. The trigger may also be shared across the Raspberry Pi GPIO header to synchronize multiple MCC 172s.
Due to the nature of the filtering in the A/D converters, there is an input delay of 39 samples, so the data coming from the converters at any time is delayed by 39 samples from the current time. This is most noticeable when using a trigger – there will be approximately 39 samples prior to the trigger event in the captured data.
Alias Rejection
At low sampling rates, certain high-frequency signals (at multiples of 128 * the sampling rate) can fall below the cutoff frequency of the fixed analog anti-aliasing filter and create aliasing in the data. Using transducers with a bandwidth lower than 100 kHz should not affect measurement results. Sampling at 10.24 kHz or higher will also ensure that the anti-aliasing filter suppresses all signals that could alias into the data.
Firmware Updates
Use the firmware update tool to update the firmware on your MCC 172 board(s). The “0” in the example below is the board address. Repeat the command for each MCC 172 address in your board stack. This example demonstrates how to update the firmware on the MCC 172 that is installed at address 0: mcc172_firmware_update 0 ~/daqhats/tools/MCC_172.fw
Dataloggers / Data Acquisition/Voltage Datalogger Template | |
|---|---|
| # Inputs/Channels | 2 |
| LCD Screen | No |
| Software Included | Yes |
Product General Attributes | |
| Unique Features | Includes 2 coaxial cables |
| Product Height | 0.47 IN |
| Product Length | 2.56 IN |
| Product Width | 2.22 IN |
| Shipping Weight | 1.00 LBS |
| HTS/Schedule B Number | 8471809000 |
| ECCN Number | EAR99 |
| Country of Origin | Taiwan |
| Shipping Height | 4.00 IN |
| Shipping Length | 2.00 IN |
| Shipping Width | 4.00 IN |
Be the first to review “Digilent MCC 172 w/ cables – 24-Bit IEPE Measurement DAQ HAT w/ 2 Coaxial Cables for Raspberry Pi”
You must be logged in to post a review.
Manuals/Guides
Spec Sheets
| Dimensions | 2.56 × 2.22 × 0.47 in |
|---|
Related products
Our team of knowledgeable professionals is here to help you make informed decisions. Whether you need product recommendations, technical support, or guidance on your purchase, we're just a click away.
Contact Us Now:
📧 sales@nestesinstruments.com
📞 +1 (833) 763-7837
Let us assist you in finding the perfect solution!
Contact Us Now:
📧 sales@nestesinstruments.com
📞 +1 (833) 763-7837
Let us assist you in finding the perfect solution!












Reviews
There are no reviews yet.